Open Source vs. Closed Source Evaluations for AI Models
Explore the debate between open source and closed source AI evaluation. This guide examines transparency, control, support, and cost for AI models and LLMs.
1. Introduction
AI model evaluation is crucial for building trust, ensuring performance, and maintaining fairness. Whether you're working with LLMs, computer vision, or predictive models, your evaluation approach significantly impacts results.
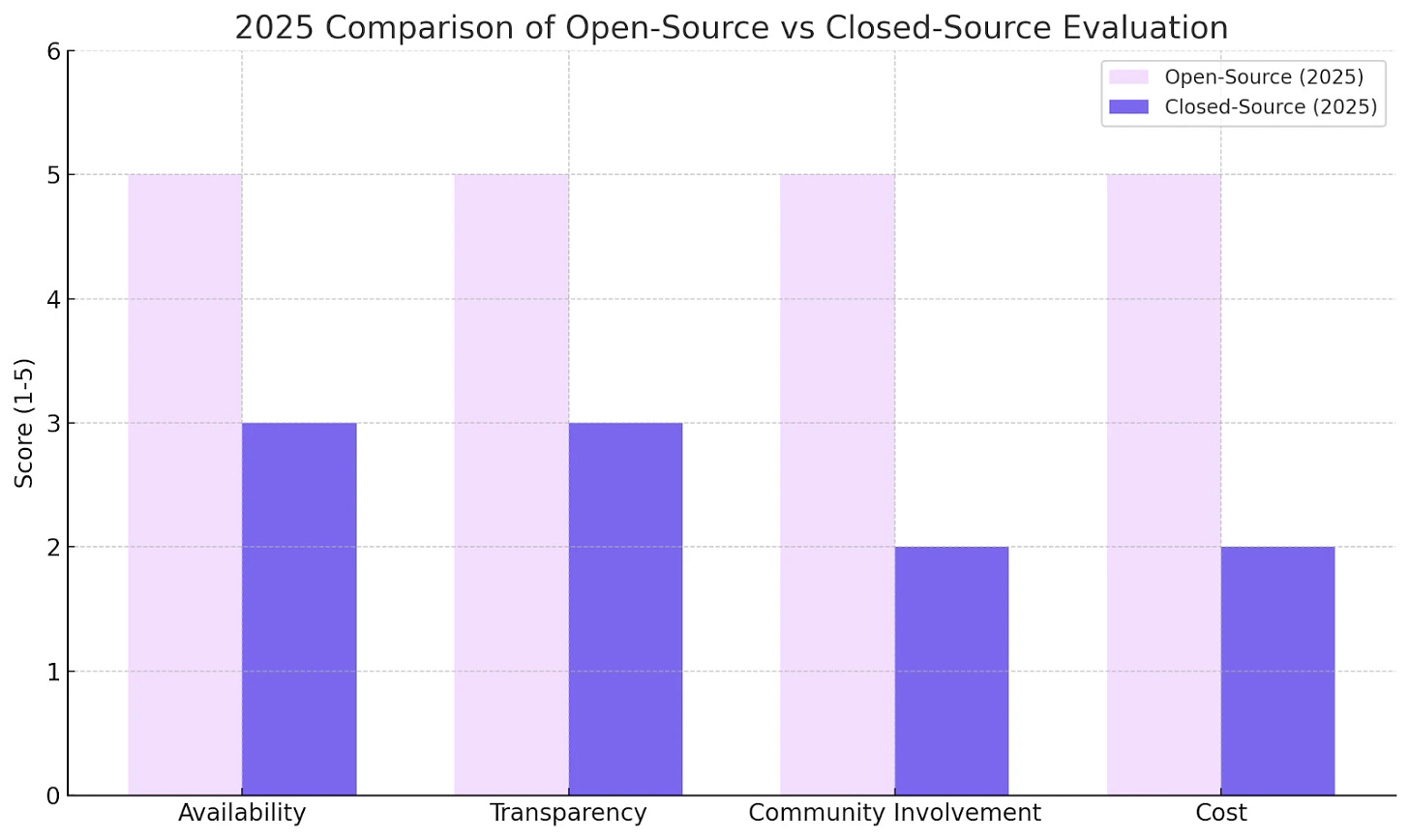
Open source evaluations offer transparency, flexibility, and community support. Closed source solutions provide enterprise support, consistency, and reliability. This guide helps you understand both options so you can make the right choice for your project needs.
2. Understanding AI Evaluations
AI evaluations systematically assess model performance, reliability, and safety. Whether you're using transformer models or rule-based systems, proper evaluation ensures your solution works effectively and without bias.
2.1 Why Do AI Evaluations Matter?
Production AI systems require evaluation for several critical reasons:
Accuracy: Does your model make correct predictions?
Reliability: Does it perform consistently across different inputs and conditions?
Fairness and Bias Mitigation: Are the outputs free from discrimination?
Transparency: Can you explain how the evaluation works?
Reproducibility: Can others replicate your results?
These factors directly impact user trust and regulatory compliance.
3. Open Source Evaluations
Open source evaluation tools give developers complete freedom and control. These community-built tools are free and regularly updated.
3.1 Examples of Popular Open Source Evaluation Tools
OpenAI Evals – Customizable framework for LLM evaluation
EleutherAI's LM-Evaluation-Harness – Multi-task language model evaluation tool
Hugging Face Evaluate – Modular library for ML pipeline integration
3.2 Advantages of Open Source Evaluations
(a) Transparency and Full Control
You can examine source code, understand metrics, and see datasets. This eliminates "black box" concerns and builds trust. Full system control allows customization and auditing, which is essential for regulated industries.
(b) Cost-Effectiveness
No licensing fees required. Your only investment is time and technical expertise. This makes high-quality evaluation accessible to startups, researchers, and institutions with limited budgets.
(c) Community-Driven Innovation
Global developer communities contribute features, fixes, and improvements. This collaborative approach accelerates innovation through rapid iterations and peer reviews.
(d) Easy Customization
Modify metrics, add datasets, and implement custom features without vendor restrictions. This flexibility ensures the tool fits your specific requirements.
3.3 Potential Drawbacks
(a) Requires Internal Expertise
Setting up and maintaining these tools isn't plug-and-play. You need skilled ML engineers, data engineers, or DevOps professionals. Without internal expertise, even simple tasks become challenging.
(b) Inconsistent Quality
Community-developed tools can have quality variations. You might encounter outdated documentation, bugs, or incomplete features. Support often relies on community forums rather than dedicated help desks.
Despite these challenges, proper planning and community engagement can mitigate most risks.
4. Closed Source Evaluations
Closed source evaluations provide stability, compliance, and service-level agreements. These commercial solutions are vendor-managed and standardized.
4.1 Leading Closed Source Evaluation Tools
Azure OpenAI Service – Enterprise evaluation tools with Azure integration
Google Vertex AI – MLOps-focused performance benchmarking
AWS Bedrock – Evaluation modules for serverless foundation models
Anthropic Claude and Future AGI Benchmarks – Safety and alignment-focused evaluation
4.2 Benefits of Closed Source Evaluations
(a) Standardized Benchmarks
Pre-built metrics and curated datasets enable easy performance comparisons. Teams spend less time building evaluation pipelines and more time analyzing results.
(b) Robust Support
Dedicated support teams provide expert consultation, documentation, and troubleshooting. This professional assistance reduces risk and increases confidence in mission-critical applications.
(c) Enterprise Integration
These platforms integrate seamlessly with existing cloud services, security protocols, and data pipelines. This compatibility simplifies deployment and ensures compliance with IT policies.
(d) Minimal Overhead
Vendors handle system maintenance, updates, monitoring, and bug fixes. This reduces operational burden and lets internal teams focus on core objectives.
4.3 Challenges of Closed Source
(a) Vendor Lock-in
Dependence on provider infrastructure and APIs makes switching difficult and expensive. This creates long-term reliance that limits flexibility.
(b) High Cost
Licensing fees and usage-based pricing can escalate quickly. This makes adoption challenging for startups and budget-conscious organizations. However, Future AGI offers evaluations at one-sixth the cost of leading alternatives.
(c) Limited Flexibility
Customization options are restricted. You can't modify core features or add custom metrics easily, limiting adaptation to unique requirements.
5. Key Factors to Help You Choose
5.1 Team Expertise & Capacity
Open Source: Best for teams with ML engineers, data scientists, and DevOps expertise.
Closed Source: Ideal for companies wanting to outsource complexity and focus on outcomes.
5.2 Customization Needs
Open Source: Provides complete control over evaluation processes.
Closed Source: Offers predefined workflows that may not suit specialized use cases.
5.3 Budget Constraints
Open Source: No licensing costs but requires implementation time and effort.
Closed Source: Higher financial investment with managed services and support.
5.4 Transparency & Explainability
Open Source: Fully transparent, essential for academic research and regulated domains.
Closed Source: Often opaque, which may be problematic for sensitive applications.
5.5 Compliance & Regulatory Needs
Open Source: Supports explainability and auditability requirements.
Closed Source: Provides certifications and assurances but lacks transparency.
6. Use-Cases: When to Pick Which
6.1 Scenarios Favoring Open Source Evaluations
Open source tools work best when you need flexibility, transparency, and cost control:
(a) Startups & Small Teams
Bootstrap AI startups can achieve powerful evaluations without licensing costs. This enables rapid experimentation and iteration.
Example: An AI startup building a niche language model uses OpenEval to test and optimize their model at no cost.
(b) Academic Research
Research requires transparency and reproducibility. Open source tools provide full access to code, metrics, and datasets for peer review.
Example: University researchers evaluating multilingual LLMs use EleutherAI's evaluation tools for transparent, replicable results.
(c) Model Innovation
Custom model architectures and novel evaluation methods require unrestricted customization capabilities.
Example: An XAI research team customizes open source evaluators with new interpretability metrics.
6.2 Scenarios Favoring Closed Source Evaluations
Closed source platforms suit organizations needing stability, support, and scalability:
(a) Enterprises
Large companies need scalable, consistent solutions across multiple teams. Closed source tools integrate with existing infrastructure and provide centralized monitoring.
Example: A global retailer uses Google Vertex AI to evaluate LLMs across product, support, and analytics teams. Alternatively, Future AGI provides high-quality evaluation at one-sixth the cost, helping one client benchmark GPT-4o, Claude Sonnet 3.5, and Mistral Large in three days. Read our case study.
(b) Regulated Industries
Healthcare, finance, and government sectors require documentation, certifications, and SLAs for compliance.
Example: A financial institution uses AWS SageMaker for fraud detection model compliance and audit reporting. Future AGI also provides enterprise-grade security with SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR certifications for compliance evaluation at lower costs.
(c) Mission-Critical Applications
Real-time systems and customer-facing applications need guaranteed uptime, security, and 24/7 support.
Example: A cybersecurity company uses Microsoft Azure ML for threat detection model monitoring with enterprise reliability.
7. Hybrid Approach - Best of Both Worlds?
Why choose one when you can use both? Hybrid evaluation strategies are becoming standard practice.
How to Build a Hybrid Model
Use Open Source Tools during R&D: Perfect for prototyping, experimentation, and community benchmarking.
Adopt Closed Source Evaluations in Production: Essential for robust reporting, auditing, and regulatory compliance.
This approach maximizes innovation while ensuring enterprise reliability and compliance.
Summary
Choosing between open source and closed source AI evaluations is a strategic decision, not a technical limitation. Open source provides freedom, control, and cost savings. Closed source offers support, scalability, and compliance readiness.
Your choice should align with your team's expertise, budget, and regulatory requirements. Often, combining both approaches gives you innovation agility and enterprise certainty.
Need help measuring your AI model's real-world performance? Future AGI's experts create advanced evaluation frameworks that deliver measurable impact. We can help optimize your strategy and improve results. Contact our team today to start evaluating more effectively.
FAQs
What are the main differences between open source and closed source AI evaluation tools?
Open source: Free, transparent, customizable, requires technical expertise. Closed source: Paid, vendor-supported, standardized, enterprise-ready.
Can I use open source evaluation tools for commercial AI products?
Yes, most open source tools allow commercial use. Check the license first - MIT and Apache 2.0 are usually fine, GPL may require code disclosure.
Are closed source AI evaluation tools more secure than open source ones?
Not necessarily. Closed source tools have built-in security and vendor updates. Open source tools can be equally secure with proper implementation, regular audits, and good access controls.
How do I decide which approach is best for my team?
Consider your team's technical skills, budget, and customization needs. Technical teams with tight budgets: open source. Enterprise teams needing support and compliance: closed source. Many use both - open source for development, closed source for production.