Manus AI: A Deep Dive and Comparison with Other AI Agents
This blog covers Manus AI's architecture, sandbox environment, GAIA benchmark results, and practical use cases across coding, research, and automation.
Ever wondered if you could start a project and let an AI take care of everything behind the scenes? A new kind of AI agent, which has generated a lot of conversation even before its release, operates on this concept.
You might’ve heard of Manus AI before, but how much do you actually know about it?
Manus AI is built to support developers and tech-savvy folks who want to get more done with less manual work. From organizing stacks of resumes to scanning market trends or even launching a full website, Manus can carry out detailed instructions from start to finish without needing constant input.
With a cloud-native engine running the show, it’s no surprise that Manus is getting attention across the tech world.
Manus AI
Manus AI is making waves as a new platform for autonomous AI agents, designed not just to generate text but to take action and deliver real outcomes. It’s developed by a Chinese startup named Monica, which boldly brands Manus as “the first general AI ”. That’s a significant statement, especially in a landscape already filled with competing agents.
What sets Manus apart is its capacity to operate independently: it can browse the web, write and run code, generate files, call APIs, and even publish content—all based on a user-defined goal.
Unlike typical chatbots like ChatGPT, which excel at conversation and simple task handling, Manus is purpose-built to tackle more complex, multi-step workflows from start to finish with minimal human oversight.
Early testers are calling it a potential “ChatGPT Operator killer”, underscoring just how seriously the tech community is taking it.
Developers and ML engineers are closely monitoring Manus because it bridges thinking and execution.
Now that you’ve got a sense of what Manus AI is, let’s dig deeper into what it can actually do.
The Architecture Behind Manus AI
Manus AI's inner workings include an advanced, multi-agent architecture that is trained in a specialised sandbox environment. These are some of the most essential elements.
Multi-Agent System
Manus AI uses a multi-agent framework to handle complex tasks quickly and effectively. A centralised "executor" agent collaborates with specialized sub-agents, each of which is accountable for a distinct function, including planning, execution, and verification.
This design lets Manus break down tasks into manageable parts, which makes sure that tasks like searching, coding, and so on are done quickly and correctly. Manus improves overall performance by preventing any one component from becoming a bottleneck by assigning subtasks to the right agents.
Foundation Model Backbone
Manus AI is fundamentally powered by Anthropic's Claude 3.7 Sonnet, a hybrid reasoning model that is capable of both complex, step-by-step problem-solving and rapid responses. Manus is capable of processing and analyzing substantial amounts of information in a single interaction due to the model's extensive context window, which supports up to 200,000 tokens. This ability is especially useful for tasks that need significant knowledge and context awareness. Each agent summarises or passes only relevant information, preventing context overload during complicated operations.
Sandboxed Execution Environment
Each Manus session runs in its cloud sandbox, which is a Linux system. This environment contains a full autonomous web browser, a Python interpreter with libraries such as Node.js and Python, and terminal and file system access. Effectively, Manus is capable of browsing websites, executing codes, and securely creating and reading files in this environment. The sandbox lets it execute code to evaluate data or scrape information instantaneously and feed results back into the AI's environment. It can also control multiple pages like a human because it has a built-in browser based on the open-source browser-use framework.
Integrations and Extensibility
Manus uses different models and tools depending on the task, which makes its operations more flexible. Despite having a fully linked system, Manus lacks a public SDK for custom connections. Instead, it focuses on providing an optimized experience right out of the box.
Observability and Transparency
Manus AI is known for its operational transparency. In real-time, users can observe the AI's decision-making process as Manus displays a to-do list or plan of subtasks and executes them step by step on the interface. Manus also includes a "replay" capability to evaluate task completion. It creates trust and assists debugging by showing how results are achieved.
To sum up, Manus's technology base is made up of a strong LLM (Claude), a multi-agent manager design, and a large set of tools in a sandbox. This allows Manus to take a general request and break it down into specific steps (such as browsing the web or running code) and continue executing these steps until the goal is achieved. It is fundamentally a system that connects "thinking" (LLM reasoning) and "doing" (tool use). The next thing we'll look at is how this information transforms into real-world benchmarks and capabilities.

Performance and Benchmarks of Manus AI
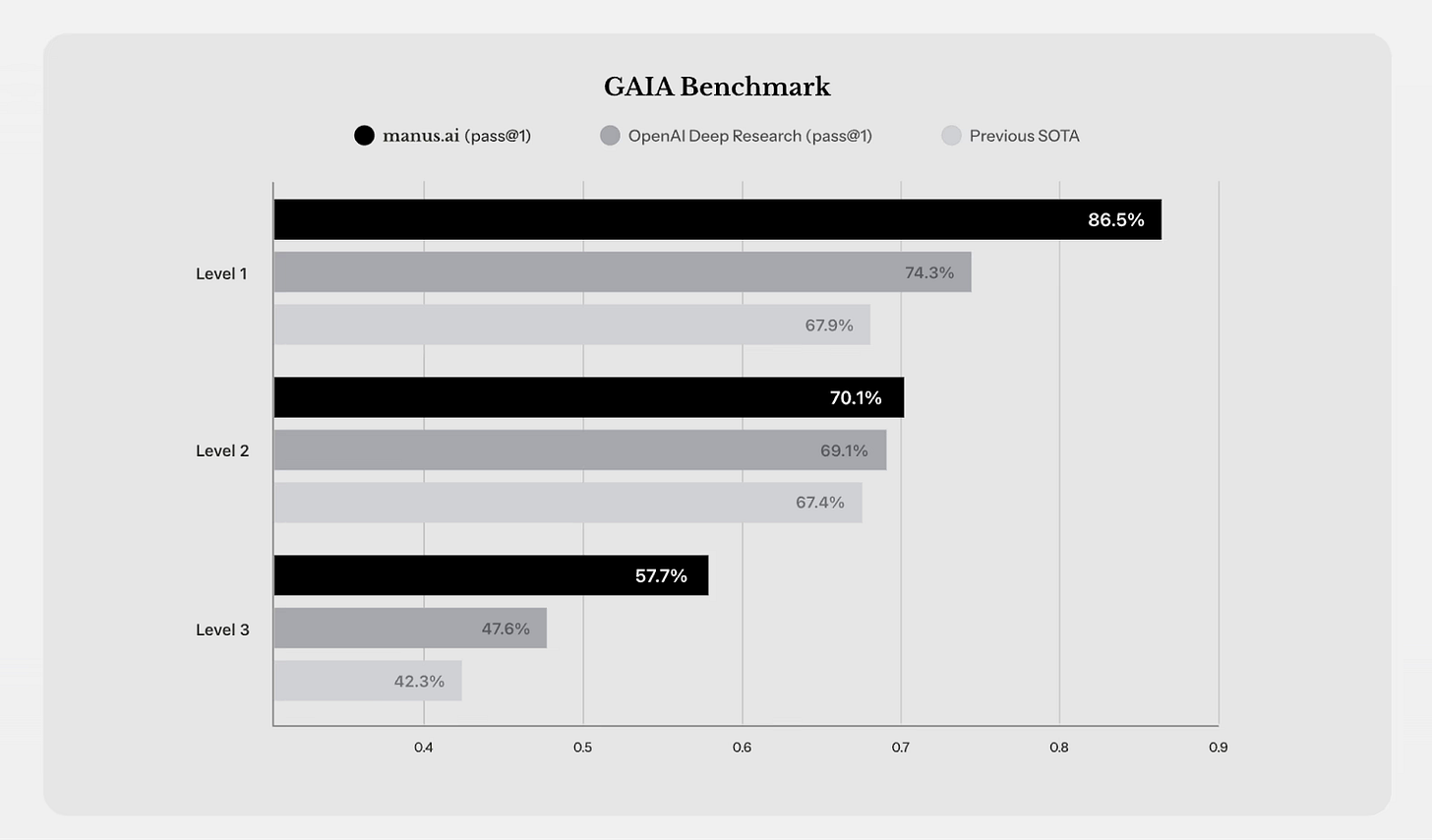
Manus performs well on demanding benchmarks, supporting its ambitious design. The team highlights Manus's accomplishments on GAIA, a new benchmark for general AI assistants that handle real-world tasks. GAIA consists of tasks that require web use, reasoning, and multi-step solutions, with differing degrees of difficulty (Level 1 being the easiest and Level 3 the most challenging). Manus got the best scores possible on all levels, doing better than systems like OpenAI's "Deep Research".
GAIA Benchmark Results: Manus AI (black) achieved a pass@1 rate of 86.5% on Level-1 tasks, surpassing OpenAI's Deep Research agent (grey) by 74.3%. Maus also outperforms its peers on more challenging Level-3 tasks (57.7% vs ~47.6%), indicating its capacity to effectively address complex, real-world challenges.
Use Cases of Manus AI
Let us briefly review the capabilities of Manus AI:
Complex Web and Code Tasks
Manus has created full-fledged online apps and games in response to early adopters. For instance, upon receiving instructions to "create a Three.js endless runner game", Manus skilfully developed a fully functional 3D endless runner game using Three.js. In another case, Manus created a Mario-style mobile game in just a few steps. Similarly, Manus replicated the visual design of the Apple homepage for web development by simply following the prompt "clone the Apple website" (although some assets were placeholders). Manus did all of these things, which usually take thousands of steps (looking for tools, making HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, etc.).
Research and Data Analysis
Manus is excellent at operations that require the examination of many different sources and the integration of insights, such as data collection and analysis. Manus's website shows an in-depth stock analysis of Tesla. A dashboard supports this analysis by displaying critical financial metrics and recommendations. The agent independently retrieved stock data, possibly using Python to manipulate numbers, and produced a result that resembled a presentation. Manus has been used to write thorough studies on climate change and market research, scouring the web for material, organizing it, and producing organized outputs.
Mixed Media and Deployment
Manus is capable of producing visual or interactive outputs in addition to text, as it can generate and deploy files. It has been observed that data visualizations, images, or diagrams are generated through code, and the resulting content is then published to a Manus-hosted web space. For example, the "Quantum Computing Learning Hub" that Manus constructed was a comprehensive mini-site that featured interactive content. Manus, for instance, can write in HTML or Markdown and publish it to show the user a live webpage. This agent offers one-click deployment, unlike any of the competitors (ChatGPT's Operator, Claude's Computer-Use, etc.).
Manus AI Vs Other AI agents
Manus AI is contrasted with three other AI agents (OpenAI Deep Research, OpenAI Operator, Claude Computer Use, and a basic Browser Use agent) in the following table, which is straightforward to comprehend. The table displays important features and details for engineers and developers.
Manus AI is different since it handles many phases at once. It displays its progress in real time, breaks down tasks into smaller components, and works on them simultaneously. OpenAI Deep Research goes into a question in more depth, but it works in a more set way, which makes it less adaptable to different projects.
OpenAI Operator responds quickly, but it doesn't explain how it works and may take a long time to finish a task. Claude Computer Use provides prompt responses within its constraints, particularly for routine data and coding tasks. The basic browser use agent doesn't integrate tools or perform additional actions; it only retrieves data from the web.
Strengths and Limitations
Manus AI is not without its shortcomings, despite its remarkable outcomes.
Strengths
It has an unmatched ability to understand and carry out complicated goals, often completing multi-step goals that would be too challenging for other agents. It is capable of effectively navigating the web, such as filling out forms and tapping on links, and its code generation is robust enough to generate functional software in multiple cases. It also offers end products such as websites, files, and reports, which go beyond simple text responses.
Limitations
Manus can be slow, delaying complex tasks for 15-20 minutes On ambitious tasks, Manus occasionally becomes stuck or fails, necessitating a restart. Large tasks may cause context overflow or loss of track, but Manus attempts to prevent this. Additionally, Manus is currently dependent on a singular underlying model (Claude) and does not have the option to transition to GPT-4 or a domain-specific model in the event that Claude experiences issues. This “closed-box” approach means that if the model output is problematic (e.g., error-filled code), the process might halt until Manus self-corrects.
Conclusion
Manus AI boasts a cutting-edge technical foundation that is highly effective for autonomous agents. Its success rate surpasses that of its competitors, as shown by benchmarks such as GAIA, and personal use cases highlight the genuine value of automation.
You can now build your own Manus-like multi-agent systems and use Future AGI’s evaluation and observability SDKs to make it production-grade, reliable, and ready to scale.
Read our documentation for more details.
For more such insights, join the conversation in the Future AGI Slack Community.




by far, the best agent
Insightful